Family Description
The violet family is a group of mostly annual and short-lived perennial dicots (sometimes woody in the tropics) which consists of approximately 18 genera-and 800 species with distribution on all continents. Leaves are simple or divided with alternate arrangement and stipules of various size. The flowers are solitary, bisexual, 5-merous with petals of unequal size. The lower pair of petals are often spurred. The flowers usually have irregular symmetry (zygomorphic). Flowers are often cleistogamous, that is self pollinated without opening. Colors are primarily in shades of blue and violet and produced in the spring. The fruit is a capsule which splits into 3 flat segments when mature.
-
The most characteristic features of the family are:
- the spurred, zygomorphic flowers
- 3-parted deciduous capsule
Plants in this family are easily grown but are effective in landscapes only in the cooler parts of the year. They are best grown in full sun or partial shade in average conditions. Propagation is primarily by seed. Seeds germinate best with soil temperatures of 55-65°F. Pest problems associated with this family are rare.
Important genera belonging to this family include Hymenanthera, Melicytus and Viola. Only Viola is common.
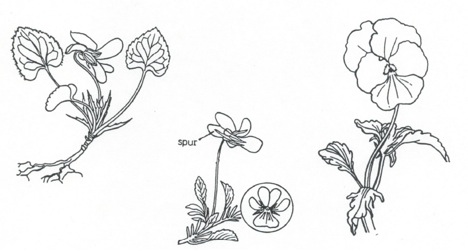
Viola odorata (left), Viola declinata (center) and Viola x wittrockiana (right)
Representative Species
| Viola oderata | Sweet Violet |
|
|||||
| * | Viola x wittrockiana
|
Pansy |
|
||||
| Viola tricolor | Johnny Jump-Ups |
|

