Family Description
The phlox family is a group of annual or perennial dicotyledonous herbs (but occasionally shrubby) consisting of approximately 18 genera and 320 species with distribution centered in the western U.S., but extending to Europe and Asia. Leaves are alternate or opposite, simple or compound. Flowers are 5-merous with petals fused into a tube; they are borne singly, in various cymose clusters, or in dense heads. Flowers have regular symmetry and are usually showy. The 5 stamens are attached to the corolla throat, often at various levels. Colors are in all shades but blues; whites and magentas are common. Flowers are produced in spring and summer. The fruit is a small capsule, usually hidden in the calyx.- The most characteristic feature:
- 5-merous flowers with petals fused forming a salverform corolla
Plants in this family are easily grown and are popular in sunny borders and rock gardens. They are best grown in well drained sites. Propagation is by cuttings, division of clumps or seed. Seeds germinate best with temperatures above 65°F. Common problems with this family are often related to poor drainage. Spider mites are sometime troublesome on some forms.
Important genera belonging to this family include Cobaea, Collomia, Eriastrum, Gilia, Ipomopsis, Langlosia, Leptodactylon, Linanthus, Phlox, and Polemonium.
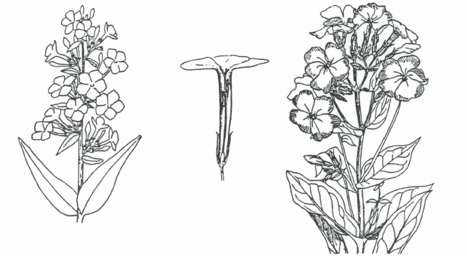
Phlox maniculata (left), Phlox flower showing stamen at various levels in the throat of the perianth tube (center), and Phlox paniculata (right).
Representative Species
click thumbnail to enlarge |
|||||||
| Phlox divaricata | Woodland Phlox |
|
|||||
| Phlox drummondi | Annual Phlox |
|
|||||
| Phlox paniculata | Perennial Phlox |
|
|||||
| * | Phlox subulata | Moss Phlox |
|
||||
| Phlox hybrids |
|

